5 Axis Volumetric Error Compensation for Large Machine Tools
System simultaneously corrects tool position in multiple axes to tighten machining accuracies on large machines that cut complex shapes.
MAG introduces a fast volumetric error compensation (VEC) system capable of analyzing and correcting positioning errors in all machine-tool axes simultaneously to achieve significantly improved machining accuracies on large parts. The MAG VEC methodology reduces the time to determine needed error compensations from days to hours, and integrates both linear and rotary axes into the tool point compensation process, according to Jim Dallam, MAG’s VEC product manager. Developed and proven by a government/industrial consortium, multi-axis VEC was conceived especially to improve machining accuracies for large machine tools needed to produce today’s large, monolithic and complex-shaped parts. The new VEC system received a Defense Manufacturing Excellence Award from the National Center for Advanced Technologies (NCAT) in December 2009. A Boeing official called it a “groundbreaking process” that will dramatically reduce assembly and fitting costs -- $100 million a year on large programs like the F-18 or 700 aircraft series.
VEC is offered as a standard option on new MAG machines and is available through MAG’s service group for field upgrade of legacy machines. “It gives plant management a practical and affordable way to raise a machine’s process capability, typically in less than a day, to meet the tighter accuracies required on new parts and programs in the aerospace industry,” said Mr. Dallam. “It’s one thing to hold tight tolerances over short distances along a linear axis, but it's far more difficult along all arbitrary contours and orientations within a volume encompassing several meters. Multi-axis VEC gives management the ability to run a large high-value part with confidence, without today’s worries, stops, checks and rework.”
Multi-axis VEC collectively treats all of a machine’s degrees of freedom that affect tool point positioning, unlike conventional calibration methods that sequentially examine machine motion one axis at time, Mr. Dallam explained. Conventional approaches to volumetric compensation are generally limited to three linear axes and the associated total of 21 potential motion error sources. However, a typical five-axis machine with linear and rotary axes can have 43 potential error sources, not just 21. MAG’s multi-axis VEC system compensates for all these, and even more, in machines with unique and more complex multi-axis configurations, he noted.
“Traditional piecemeal compensation of one axis at a time does not consider axis kinematic relationships and their effect on volumetric accuracy,” he said. “MAG’s VEC solution is unique in considering the full interrelated effects resulting from the kinematic stack-up of the machine tool axes. This holistic methodology enables volumetric error compensation for every point orientation and path combination inside the work volume.”
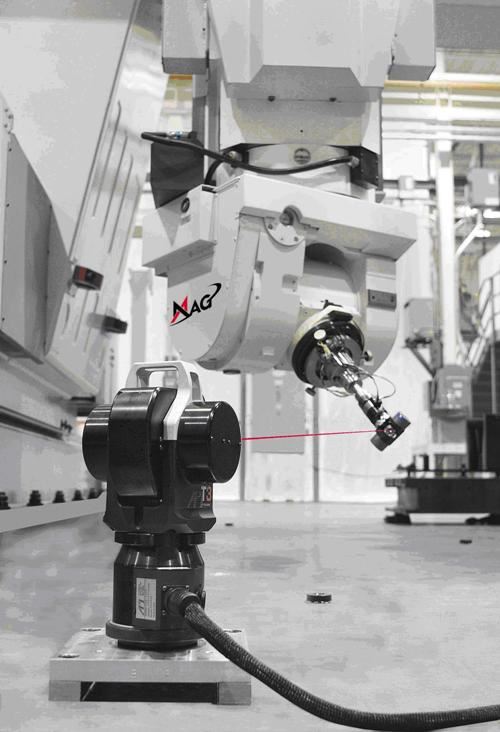
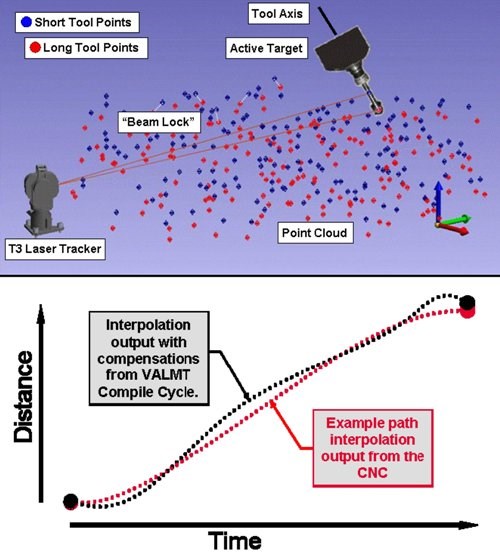
The multi-axis methodology originated in Boeing R&D, St. Louis, Missouri, and uses laser technology from Automated Precision, Inc. (API). A laser source, the T3 Laser Tracker, is placed in the work piece position. It directs the laser beam to the Active Target, mounted in the machine tool’s spindle. These interact to maintain a metrology “beam lock” during the volumetric calibration event.
To perform a VEC event, an NC program positions the Active Target to a cloud of some 200 points representing a series of statistically randomized multi-axis “poses” within the work envelope. The same NC program is run three times, Dallam explained, first with the Active Target at a long tool length, then twice again at a short tool length. The 200 commanded and measured positions from the first two runs are mathematically combined to establish each tool axis vector orientation and the third run gives a measure for repeatability. Automated software processes all pose/point data as simultaneous polynomial equations to determine volumetric compensation based on the kinematic error model of the machine.
The compensation solution is then entered into the control, where “compile cycle” technology integrates the compensations into real-time CNC path control algorithms. The volumetric accuracy compensations work in conjunction with, and on top of, traditional, underlying single axis and cross-axis comps, said Mr. Dallam.
Boeing, MAG, API and Siemens were members of the industry/government consortium that developed the VEC under the program for Volumetric Accuracy of Large Machine Tools (VALMT). Other participants were the National Center for Manufacturing Science, U.S. Air Force Logistics Center, Naval Foundry and Propeller Center, U.S. Navy Fleet Readiness Center, East, and U.S. Army Anniston Depot. The system was tested and proved out on three large machine tools offering different axis configurations.
Related Content
Fearless Five-Axis Programming Fosters Shop Growth
Reinvestment in automation has spurred KCS Advanced Machining Service’s growth from prototyping to low-and mid-volume parts. The key to its success? A young staff of talented programmers.
Read MoreWhich Approach to Automation Fits Your CNC Machine Tool?
Choosing the right automation to pair with a CNC machine tool cell means weighing various factors, as this fabrication business has learned well.
Read MoreDigital Twins Give CNC Machining a Head Start
Model-based manufacturing and the digital thread enable Sikorsky to reduce lead times by machining helicopter components before designs are finalized.
Read MoreInverting Turning and Five-Axis Milling at Famar
Automation is only the tip of the iceberg for Famar, which also provides multitasking options for its vertical lathes and horizontal five-axis machine tools.
Read MoreRead Next
3 Mistakes That Cause CNC Programs to Fail
Despite enhancements to manufacturing technology, there are still issues today that can cause programs to fail. These failures can cause lost time, scrapped parts, damaged machines and even injured operators.
Read MoreThe Cut Scene: The Finer Details of Large-Format Machining
Small details and features can have an outsized impact on large parts, such as Barbco’s collapsible utility drill head.
Read More














.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)

.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)








