How Do You Maximize Tool Life In Aluminum?
Boeing experts say climb vs. conventional is not the key. They recently answered a question submitted through our Aerospace Machining Zone, saying the key to tool life is actually chatter control.
Personnel from Boeing's Research & Technology group recently answered readers' questions. One reader asked the following.
Question
I am roughing Al 7000-series material at around 30,000 rpm using a 1-inch solid carbide uncoated end mill with 2 flutes at an axial DOC of 0.200 inch and a radial DOC of 50%. I am using an HSK80 toolholder, coolant through, with a good machine and stable setup.
At this speed, there is no surface finish difference if I climb or conventional mill. But is there a difference between the two methods in terms of tool life?
Response from Boeing’s Research & Technology group
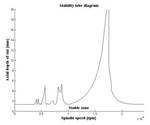
With 7000-series aluminum on our own 24,000-rpm spindle, we achieve 200+ hours of tool life using carbide cutters. We do both climb and conventional milling and we do not see tool life being affected. For us, the key to long tool life and good part finishes is dynamically testing all of our cutting tools first before high speed machining aluminum. By doing so, we find what is called the "sweet spot," which is the optimal rpm and depth of cut the cutting tool will run with no chatter regardless of step-over, full slot cutting or corners. Once we have these parameters, we program to them—confident that we will not have any cutting tool chatter issues. The system we use for this dynamic testing is called "Metal Max” from Manufacturing Laboratories, Inc.
Related Content
-
Choosing Your Carbide Grade: A Guide
Without an international standard for designating carbide grades or application ranges, users must rely on relative judgments and background knowledge for success.
-
New Modular Tool Options for Small Spindle Milling
Tooling options have been limited for small spindle milling applications. Now modular, indexable systems are available that provide broad flexibility to get the right cutter for the job with less inventory and at lower cost.
-
Best Practices: Machining Difficult Materials
Cutting hardened steel, titanium and other difficult materials requires picking the right tools, eliminating spindle runout and relying on best practices to achieve tight part tolerances.







.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)






