Indexable Mills Speed Cavity Cutting
Ballnose mills are a common choice for hogging out cavities on molds and form dies. However, these three shops have realized significantly faster cavity milling by switching to Ingersoll’s Chip Surfer modular tooling system, which features a cylindrical shape that keeps more of the tool engaged in the cut.
Any shop that chooses to hog out mold and die cavities with a solid carbide ball mill could be missing out on throughput gains available with new indexable mills, according to Ingersoll Cutting Tools (Rockford, Illinois). In fact, shops that have made the change-over have reported gains of as much as 3 to 1 in roughing and 6 to 1 in finishing, the company says. Many report improved surface finishes as well.
“Many of the new indexable tools capitalize on the fact that cavity hogging is largely side milling, explains Bill Fiorenza, die and mold tooling manager at Ingersoll. “Generally, indexable form tools are more cylindrical than spherical, so more of their active surface is moving at optimum surface cutting speed. This is not possible with spherical mills because surface speed varies with diameter.”
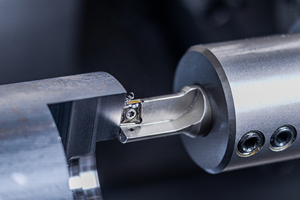
As evidence for these claims, the company cites the experiences of three shops: B&J Specialties (Wawaka, Minnesota), Crosby-Lebus (Longview, Texas) and Datum Industries (Grand Rapids, Michigan). All have switched from ballnose mills to Ingersoll’s Chip Surfer, a modular tooling system consisting of a ductile alloy steel shaft and a variety of replaceable, hard carbide cutting tips.
A key point is that speeding cavity milling isn’t just an end in and of itself. Cavity work makes up a large portion of the cost of producing molds and form dies. The shop that speeds up this operation can quote faster delivery times and lower prices while still maintaining profits, Mr. Fiorenza says. Likewise, captive die shops can turn around repairs much quicker, thereby delivering its forgings or stampings sooner.
The following provides a closer look at the Chip Surfer and how these shops have employed the tool to realize these advantages in their cavity milling operations.
Everybody’s Going Surfing
The primary key to the Chip Surfer’s effectiveness is its cylindrical geometry, which leverages chip thinning and places more of the active cutting surface near the full radius to cut at optimum speed, the company says. This aids in producing square shoulders and flat, bump-free bottom surfaces. In contrast, the only part of a spherical ball mill engaged in cutting action is its equator.
Putting the carbide only where it’s needed—at the cutting edge—reduces tool costs, the company says. A single shank can accommodate the full range of replaceable tips, which can be quickly changed out while in the spindle at 0.0005-inch repeatability. “You can replace worn tips or switch from roughing to finishing tips without losing datum,” Mr. Fiorenza notes.
Additionally, the ductile alloy steel shaft makes the tool more forgiving of vibration and high side loads, especially during interrupted cuts. At B&J, Crosby-Levus and Datum, this has eliminated the need to slow down around corners and internal curves — features that all three shops cite as constituting a large portion of the cycle time on a typical mold or form die.
B&J: Faster Roughing and Finishing
B&J Specialties focuses on large mold sets for appliance and automotive manufacturers. Typical materials machined here include hardened A-2 stock as well as wrought H-13 and M-4 steel. The shop’s workhorse CNC machine is a Makino V 550 with a 20,000-rpm spindle and table speed to spare. In fact, before changing tools, the shop had to slow things down to avoid dulling or snapping its carbide ball mills every 10 minutes.
With the Chip Surfer’s toroidal high feed tip in place, the shop roughs the cavities at 200 ipm, 3,750 rpm and an 0.012-inch cutting depth. That’s an 8-to-1 gain in throughput compared to the previous ball mill, which ran at the same spindle speed but only 100 ipm and an 0.004-inch cutting depth,
Using the Chip Surfer’s toroidal high feed tip, the shop increased cavity roughing feed rates from 100 to 200 ipm and cutting depth from 0.004 inch to 0.012 inch (both the Chip Surfer and the old ball mill ran at a spindle speed of 3,750 rpm.) That’s an 8-to-1 gain in the corners as well as the straightaways. For finishing, the shop switches to a bullnose tip—a simple, 20-second operation performed while the threaded shank is still in the spindle—and increases the feed to 700 ipm. The next tip picks up where the previous one left off, within 0.0005 inch. Additionally, the shop has found that repeatability among tip is sufficient to eliminate the need for offsetting or touching off.
Crosby-Lebus: Machining Hardened Forging Dies Twice as Fast
Crosby-Lebus supports a forging operation that turns out parts for giant cranes. A typical forging is a rugged, 200-pound crane hook. Much of the machining here consists of repair work on hardened dies. The shop has standardized on a ¾-inch Chip Surfer high feed cutter for die gutters and flash lands as well as cavities.
Typical parameters for the shop’s previous cutter, a ¾-inch carbide ball mill, were 30 ipm, 1,250 rpm and a 0.01-inch cutting depth with stepover ranging from 0.03 to 0.05 inch. In contrast, the Chip surfer enabled increasing the standard feed rate to 50 ipm and significantly reducing stepover. As a result, the metal-removal rate doubled. “The as-machined finish is good enough to completely eliminate polishing,” says C-L programmer Buddy Walston. “Remember, the parts we make aren’t particularly appearance-sensitive.”
Datum: Taking Corners at Speed
Datum first tried the Chip Surfer high feed mill on a narrow, deep cavity that created problems for its ball mills. These tools always left a bump at the bottom of the cavity, necessitating additional operations to smooth it.
In contrast, the new tool leaves the bottom completely flat and completes the slot in one-third of the time. Of course, the benefits extend beyond that specific job. Since retooling, the shop says it has been able to feed 10 times faster for all cavity work. Standard settings are 400 ipm, 3,855 rpm and an 0.2-inch cutting depth. “The most pleasant surprise is the speed in and out of corners,” says process engineer John Smith. “We don’t have to slow down, and we are left with a square corner and a perfectly flat bottom.”
The shop also reports a 25-to-1 gain in tool life, and it has eliminated semi-finishing operations. Another Chip Surfer tip, the bullnose, has replaced EDM for roughing pedestal punches. Using the tool to mill these parts to within 0.02 inch of final size has reduced cycle time and eliminated a second setup.
“Many programmers brought up on ball mills slow down in the corners out of habit, or they’re afraid of snapping the tool due to higher lateral loads or chip jamming at that point in a tool path.” Mr. Fiorenza says. “Not so with John Smith. He capitalizes fully on a tool geometry that favors the “feed fast, cut shallow” strategy, and he practices it everywhere possible—even in the corners and internal curves. The results speak for themselves.”
Related Content
10 Tips for Titanium
Simple process considerations can increase your productivity in milling titanium alloys.
Read MoreHow to Tackle Tough Angled Pocket Milling With Two Tools
Milling a deep pocket with a tight corner radius comes with unique challenges, but using both a flat bottom drill and a necked-down finishing tool can help.
Read MoreCeratizit's Updated Tooling Solutions Improve Machining Performance
The company has upgraded its EcoCut indexable inserts lineup, as well as introduced two new toolholding and workholding solutions.
Read MoreNew Modular Tool Options for Small Spindle Milling
Tooling options have been limited for small spindle milling applications. Now modular, indexable systems are available that provide broad flexibility to get the right cutter for the job with less inventory and at lower cost.
Read MoreRead Next
3 Mistakes That Cause CNC Programs to Fail
Despite enhancements to manufacturing technology, there are still issues today that can cause programs to fail. These failures can cause lost time, scrapped parts, damaged machines and even injured operators.
Read MoreThe Cut Scene: The Finer Details of Large-Format Machining
Small details and features can have an outsized impact on large parts, such as Barbco’s collapsible utility drill head.
Read More









.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)