Separator Solves Tramp Oil Dilemma
Debco Machine, Inc. (Natick, Massachusetts), a job shop specializing in precision components from aluminum, plastics and stainless steel, was faced with what it characterized as a particularly demanding requirement for tramp oil removal from the sump of a Matsuura 510 vertical machining center, a machine that is in nearly constant use. About 1 gallon per day of tramp oil enters the 100-gallon coolant sump of this machine.
Debco Machine, Inc. (Natick, Massachusetts), a job shop specializing in precision components from aluminum, plastics and stainless steel, was faced with what it characterized as a particularly demanding requirement for tramp oil removal from the sump of a Matsuura 510 vertical machining center, a machine that is in nearly constant use. About 1 gallon per day of tramp oil enters the 100-gallon coolant sump of this machine.
Parts produced by the company are incorporated in robotic devices, dissolution machines used in the development of drugs, respirators, soldering devices and other applications requiring tight tolerances. Debco runs at full capacity, even during slow periods. To this end, there is no time available for machines to be off-line for cleaning and adjustment.
Dan Collari, owner and shop manager, was particularly concerned with maintaining the productivity of the machining center, realizing that the presence of a large quantity of tramp oil in the coolant was adversely affecting machine throughput, tooling life and parts finish.
“This particular Matsuura machine is online continually,” says Mr. Collari. “It does a little bit of everything, which can lead to problems. We may have a precision stainless steel job following one involving plastics or aluminum, leaving a considerable quantity of suspended chips and fines in the coolant.”
If the coolant is not cleaned routinely, then the plastic or aluminum solids are picked up by the coolant pump and sprayed onto the precision stainless working part. A further complication is that the 100 gallon sump is divided into three compartments, and removing the tramp oil from only one compartment—for example, using a conventional belt skimmer—does not reduce the oil in the other compartments.
Mr. Collari says the problem required immediate attention, given the significance of the machine. He surmised that using a dedicated separator, rather than a portable unit that would treat all of the machines in the shop sequentially, was the most appropriate course of action. Familiar with conventional separators, Mr. Collari concluded that they would not be suitable to address the shop’s dilemma. Another requirement was that the separator should require little or no attention from the machine operator, the company says.
“When an operator who has worked an 8 or 9 hour shift suddenly sees that the coolant cleaner has plugged or is flooding, he/she may be tempted to shut down the unit and forget about it,” speculates Mr. Collari.
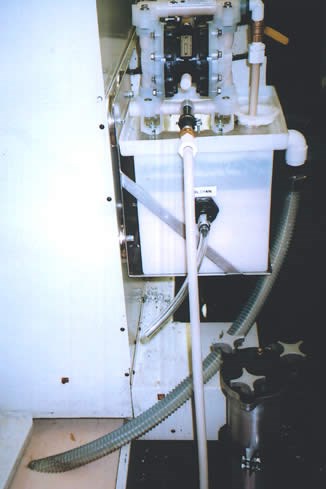
Belt skimmers and disc skimmers do not remove floating solids; they do not circulate the coolant to clean all segments of the large sump, says the company. Among other candidates, the Model TKO-6, part of a family of separators for individual sumps offered by Keller Products, Inc. (Acton, Massachusetts), was evaluated as a potential solution.
Having used portable Keller units on other machines for several years, Mr. Collari says he was quite familiar with the company’s line of separators. The model TKO-6 possesses several features that made it suitable for this application, particularly the fact that it is equipped with a 1/2-inch compressed, air-operated diaphragm, says the company.
According to the manufacturer, the inclusion of 1/2-inch pump, as opposed to the 1/4-inch diaphragm pumps or electric pumps used on small separators, is conducive to enhancing performance and reliability. The pump enables the separator to readily deal with the large volume of tramp oil in this particular sump. The flow rate of 3 gpm, which continually turns over the 100-gallon sump nearly twice per hour, aerates the coolant and creates vigorous circulation, in turn forcing oily coolant to the inlet device from all areas of the sump. The flow rate through the oil separation section can be modulated to obtain a clean split of tramp oil from a slow-rejecting coolant without affecting the overall coolant recirculation rate.
“Maintenance of a 1/4-inch diaphragm pump is no picnic,” says Mr. Collari. “I’ve found that the 1/2-inch pump keeps running, without maintenance being an issue. In addition, the model’s 14-inch by 14-inch footprint is crucial because of the limited floor space in the shop.”
Containing no replaceable parts, the separator can be set up when the user clamps the inlet device to the filter inlet using the hose provided. According to the manufacturer, the filter on the inlet side is a common feature to all of its oil separators and can protect the pump from damage by chips and other solid particles. In addition, the permanent plastic oil separation element does not require cleaning or replacement.
The collected tramp oil is drained from the separation tank by opening the drain valve briefly, usually once per day, according to the company. The prefilter screen is cleaned once every 2 weeks—about a 5-minute task.
Happy with the separator’s performance, Mr. Collari reports that the Matsuura is operating at optimum efficiency and that his staff no longer wastes time tinkering with the coalescing unit.
Related Content
Rego-Fix Toolholding System Reduces Coolant Consumption
MQL PG collets are designed for machines using one-channel, internal through-spindle MQL systems.
Read MoreVomat Coolant Filters Provide Precise Temperature Control
The company’s filters ensure a continuous supply of clean oil for microtool grinding applications.
Read MoreManaging Coolant with Skimmers, Refractometers and More
Bacteria-infected coolant harms machines and sickens machinists. Coolant management technologies like skimmers and automated systems counter this tendency.
Read MoreSTLE To Host Metalworking Fluid Management Program
STLE’s program is a two-and-a-half-day education program offering a comprehensive overview of metalworking fluid management.
Read MoreRead Next
The Cut Scene: The Finer Details of Large-Format Machining
Small details and features can have an outsized impact on large parts, such as Barbco’s collapsible utility drill head.
Read More3 Mistakes That Cause CNC Programs to Fail
Despite enhancements to manufacturing technology, there are still issues today that can cause programs to fail. These failures can cause lost time, scrapped parts, damaged machines and even injured operators.
Read More
















.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)









