With Face Drivers, Shop Faces Long Cycle Times Head On
By switching from jaw chucks to face drivers, a manufacturer of large shaft components was able to reduce the number of setups, cutting cycle times on some parts from days to hours.
Reducing the number of setups it takes to machine a part can improve both quality and cycle time. When Johnson Machine Works began investing in technology to improve quality and reduce cost per part, it discovered that by switching the workholding on its new multitasking lathe from chuck jaws to face drivers, it could reduce the number of setups for some of its larger parts, chopping cycle times from days to hours.
Johnson Machine Works has been in business in Chariton, Iowa, since 1907. Originally a repair shop for local farmers, the company has grown into a fabricator of large steel structures with clients all over the world.
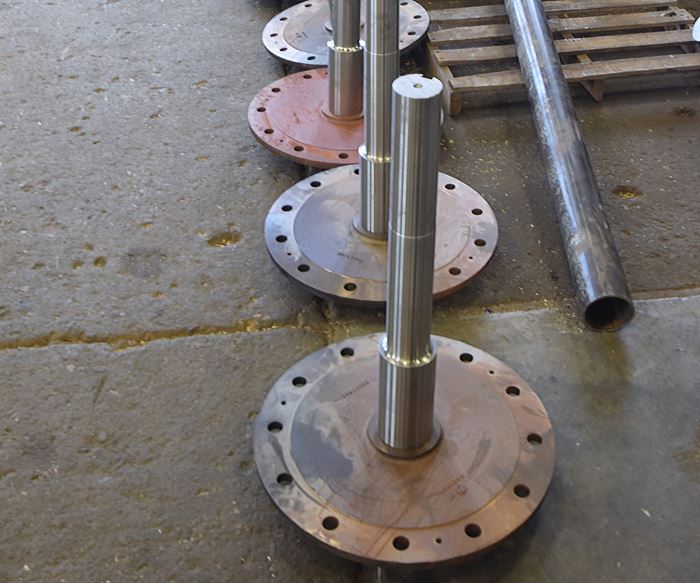
For years now, the shop has manufactured a range of large carbon steel and stainless steel shafts for various customers. Many are designed for use in critical applications and have tight tolerances for runout from end to end. One family of flanged parts is representative of the extensive setup and machining time that was required. A typical part in this family has a 2-inch-thick flange that measures 23.5 inches in diameter and a 6-inch-diameter shaft that is 45 inches long. The part’s runout tolerance might be +0/-0.001 inch. After two initial turnings on manual lathes, the shafts would undergo a horizontal keying operation before they were moved into a vertical position for drilling flanged bolt holes. Many of these steps required flipping the shaft around and reclamping it in a fixture or chuck. This often resulted in parts that exceeded allowable dimensional tolerances, requiring additional setup and machining time to restore accuracy. For some of the larger flanged shafts, the process to complete a single part would take as many as five days.
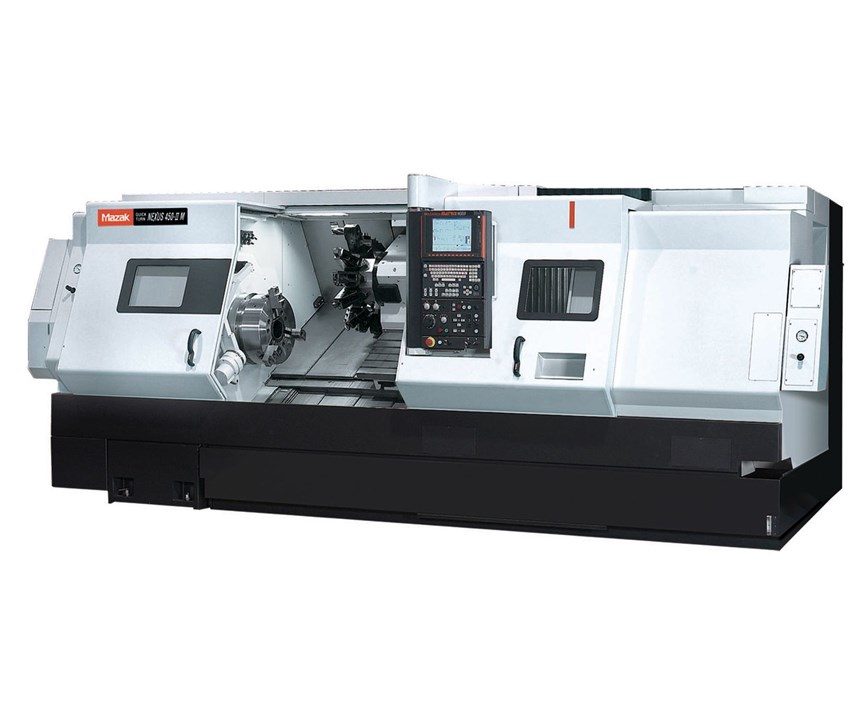
In need of a more efficient solution, Plant Engineer Kelley Werts reached out to Curt Block, Mazak’s Iowa sales manager, for an equipment evaluation. This grew into a process analysis, and in 2014, the shop purchased a Mazak Quick Turn Nexus 450M with live tooling capabilities. The new machine could reduce turning time, but the shop still needed to address the drilling and keying operations.
At Mr. Block's suggestion, Johnson Machine Works contacted Dan Reasoner of the Whittemore Co., the region’s representative for Riten Industries (Washington Court House, Ohio), who recommended that the shop replace its chuck jaws with face drivers for workholding.
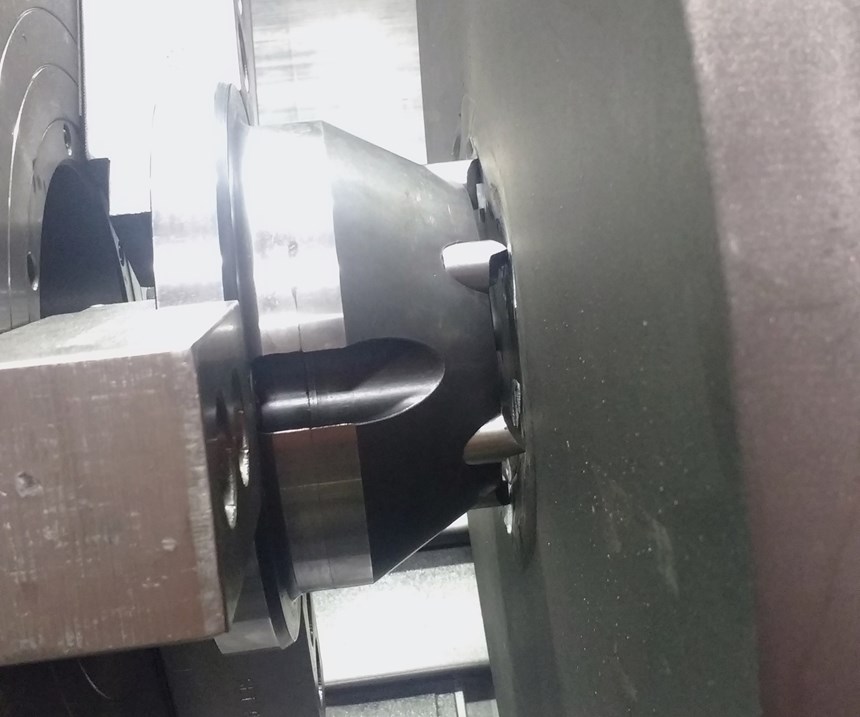
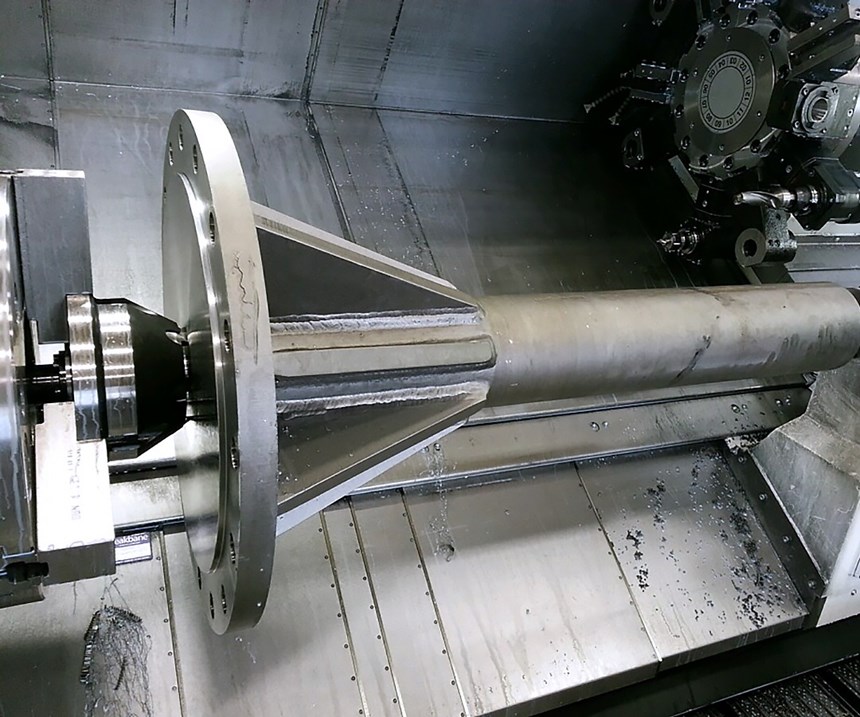
Face drivers employ chisel-edged drive pins that bite deeply into the end face of the workpiece under pressure from the tailstock and the cutting forces generated during initial machining. In contrast with chuck jaws, face drivers leave the entire length of a workpiece exposed for machining, eliminating the need for reclamping. This saves time and results in concentricity between centers, improving surface finish. With sufficient tailstock pressure, the correct drive-pin edge width and proper cutting tool forces, a face driver is designed to safely hold large parts: an important requirement for Johnson Machine Works.
The company chose two large, standard face drivers from Riten Industries—a flange mount and a 5 Morse taper mount—that accommodated the entire range of shaft sizes. With the correct selection of center points and drive pins, the face drivers could supply the required gripping force on all the necessary parts.
Mr. Reasoner was confident that the face drivers not only would be up to the task of aggressive turning, but that they would also enable the Mazak machine to perform secondary milling operations. What the shop previously had done on four machines could now be done on one—in a single setup—saving time and improving surface finish.
Because Johnson Machine Work's machinists limited experience with face drivers, only using them on older equipment to make smaller parts, Mr. Reasoner supervised the installation and machined a sampling of shafts of various sizes. He stayed with the operators until they were comfortable using the face drivers.
After a period of testing and adjustment, the new process proved to be a success. “This new setup has completely changed our approach to large-shaft machining,” say shop manager Tyler Ruepke. “The change-over from one shaft to the next is quick and easy. The quality is superior to our previous methods and the cycle time has been reduced from days to hours.”
According to Mitchell Kirby, Riten’s vice president of manufacturing, the 32-RMS surface finish the parts require is easier to hold with the new lathe and face drivers in comparison to the older equipment.
Initially, the face drivers were intended to machine screw pump shafts, but today the shop is using them for a variety of shafts in all areas of the business.
Related Content
An Additive Manufacturing Machine Shop
Finish machining additively manufactured implants requires different pacing and workflow than cutting parts from stock — different enough for an experienced manufacturer to warrant a dedicated machine shop.
Read MoreA Case for Combining Workholding with Optical Scanning
Automotive dies and die inserts are often complex, one-off parts with little room for error. Integrity Tool's investments in modular workholding tools and 3D optical scanning have allowed the company to create niche capabilities for its CNC machined parts.
Read MoreWhen To Use A Collet Chuck
Don't assume the standard chuck is the right workholding for every lathe application.
Read MoreModern Bar Feeds Bring New Life to Automatic Swiss Lathes
Cam-actuated Swiss lathes are still the fastest way to process many parts. By adding modern bar feeders, this shop has dramatically improved their utilization with the ability to work unattended, even in a lights-out environment.
Read MoreRead Next
3 Mistakes That Cause CNC Programs to Fail
Despite enhancements to manufacturing technology, there are still issues today that can cause programs to fail. These failures can cause lost time, scrapped parts, damaged machines and even injured operators.
Read MoreThe Cut Scene: The Finer Details of Large-Format Machining
Small details and features can have an outsized impact on large parts, such as Barbco’s collapsible utility drill head.
Read More.jpg;maxWidth=970;quality=90)












.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)



.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)