For some shops, sawing workpiece blanks might be an afterthought. That said, greater efficiency can be built into a machining process by considering ways to become more effective at this preliminary step to machining parts on mills and lathes, which is possible with new smart-manufacturing technology from Cosen Mechatronics (known as Cosen Saws USA here in the United States, and located in Charlotte, North Carolina).
What’s ironic is that I traveled halfway around the world to discover that the roots of this technology are planted in my neck of the woods in Cincinnati, Ohio, at the University of Cincinnati’s Center for Intelligent Maintenance Systems (IMS). It was a nice bit of serendipity learning about this from Alice Wu, CEO of Cosen Mechatronics, when I recently visited the company in Taichung, Taiwan.
IMS was started by Dr. Jay Lee, the center’s director, who was researching prognostics and health management (PHM) with an eye toward ensuring zero-breakdown performance for industrial equipment. Today, the IMS Center is a National Science Foundation industry/university collaborative that consists of the University of Cincinnati (UC), the University of Michigan and the Missouri University of Science and Technology. Since 2001, the Center has conducted more than 100 projects in partnership with more than 100 international organizations, including Toyota, Boeing, Bosch, Caterpillar, GE Aviation, Goodyear, Harley-Davidson and Siemens.
Its goal is to develop systems that would enable equipment of various types to achieve and sustain zero-breakdown performance while offering more accurate predictive maintenance scheduling. Its Watchdog Agent toolbox is the center’s collection of tools and methods for PHM. It includes four categories of analytical tools—health assessment, health diagnosis, signal processing and feature extraction, and performance prediction—that can be customized for a variety of applications.
Cosen started working with IMS nearly four years ago. Ms. Wu says the company’s goal was to eliminate the need to track machine hours and accumulate cut data to get a rough idea as to when a blade might need to be replaced. By being able to predict when a blade might fail, manufacturers can better prepare for and schedule planned maintenance downtime and eliminate the risk of a surprise blade failure.
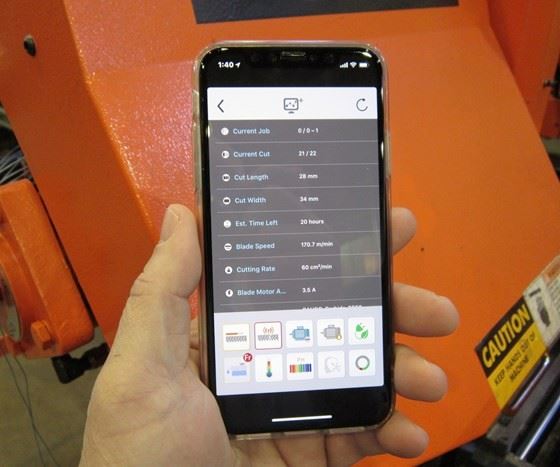
The company delivered one of its CNC band saws to UC to enable the IMS team to perform various test cuts. Accelerometers installed on the machine were used to monitor vibration during operation. Excessive vibration is a telling sign that a band saw blade is wearing or a tooth (or teeth) is chipped. The resulting SawLogix app was introduced at the last International Manufacturing Technology Show (IMTS).
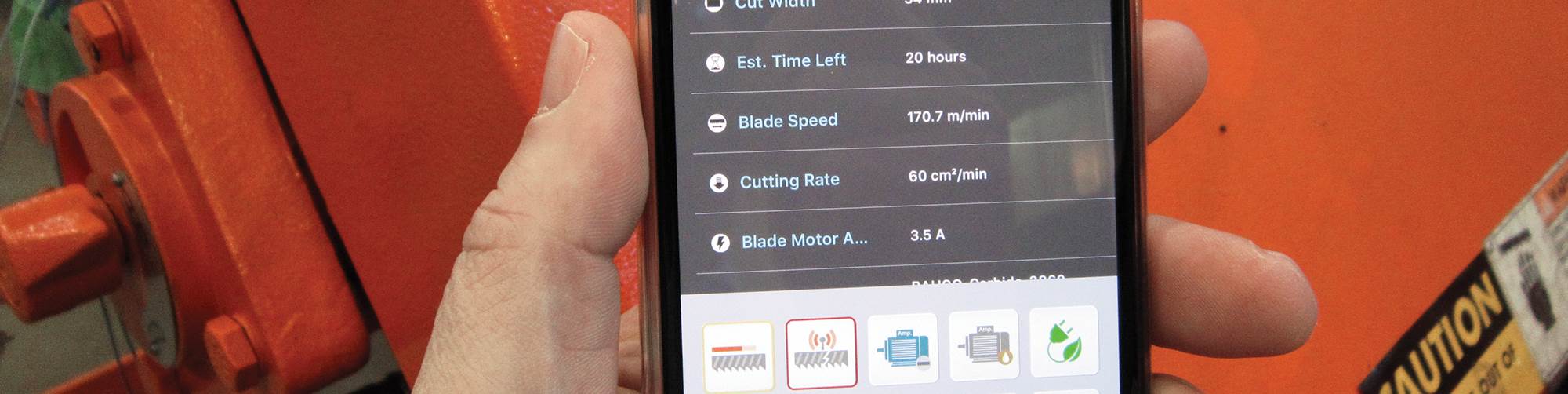
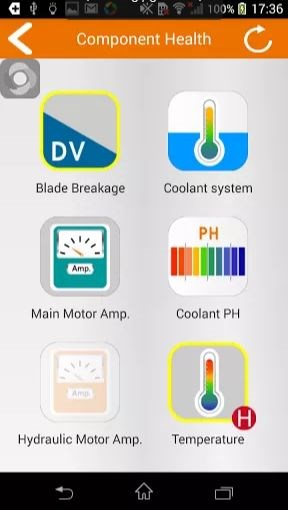
Along with predicting blade life, this app also enables real-time monitoring of various parameters such as machine status, number of cuts performed, time remaining to complete a job, etc. and is accessible on smartphones and tablets. It can send alerts, too, such as when the last piece of a job has been cut and the material is ready to be picked up. With additional sensors, the app can monitor and track parameters such as coolant, environmental, gearbox and hydraulic-fluid temperature; coolant pH and flow rate; and motor amperage.
SawLogix can be retrofitted to existing Cosen saws as well as other brands of computer numerical control (CNC) saws. In addition, Cosen has started another business, MechaLogix, to explore similar cloud-based predictive monitoring apps for other types of CNC machines.
Related Content
Reinventing a Precision Shop With a Data-Driven Mindset
When this machine shop lost 90% of its business within three months, a reinvention was in order. Here's how it survived after quickly falling on hard times.
Read MoreSwiss-Type Control Uses CNC Data to Improve Efficiency
Advanced controls for Swiss-type CNC lathes uses machine data to prevent tool collisions, saving setup time and scrap costs.
Read MoreWireless Couplers Work Wonders for Workholding
Possibilities range from individual control of chuck jaws and tombstone fixtures to more reliable robots.
Read MoreBeyond the Machines: How Quality Control Software Is Automating Measurement & Inspection
A high-precision shop producing medical and aerospace parts was about to lose its quality management system. When it found a replacement, it also found a partner that helped the shop bring a new level of automation to its inspection process.
Read MoreRead Next
The Cut Scene: The Finer Details of Large-Format Machining
Small details and features can have an outsized impact on large parts, such as Barbco’s collapsible utility drill head.
Read More3 Mistakes That Cause CNC Programs to Fail
Despite enhancements to manufacturing technology, there are still issues today that can cause programs to fail. These failures can cause lost time, scrapped parts, damaged machines and even injured operators.
Read More
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)

















.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)