New Grinding Machine Utilizes Unique Kinematics
A novel grinding machine uses three rotary tables stacked off-center to provide full control over the grinding wheel’s X and Z axis, as well as its angular position, creating an unusual solution to grinding.
Share



Phillips Corporation - Education
Featured Content
View More




Phillips Corporation
Featured Content
View MoreManufacturing is about constant improvement. Just as machine shops work hard to improve the speed at which they get parts out the door without losing quality, OEMs have thousands of people dedicated to improving manufacturing equipment to make their customers’ jobs easier. In this flurry of innovation, the most common approach is to improve on existing solutions to problems: increase the rigidity of a five-axis table, get more tool life out of an end mill or otherwise improve on technology that is currently in use.

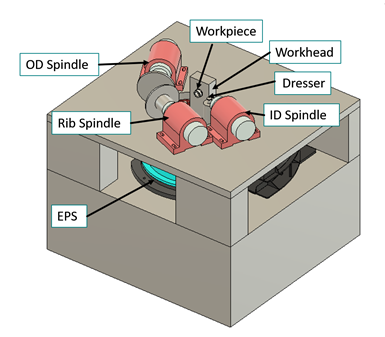
The EPS uses three rotary tables stacked off-center. The tables rotate to adjust the position of the grinding wheel, enabling both precise grinding and eliminating the need for form dressing. Photo Credit: Coventry Associates
But then, sometimes there are attempts at entirely new solutions as well.
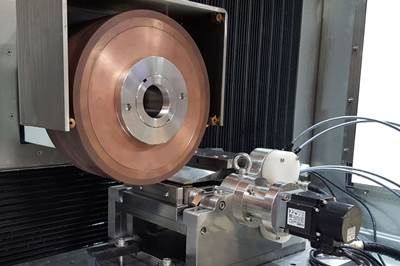
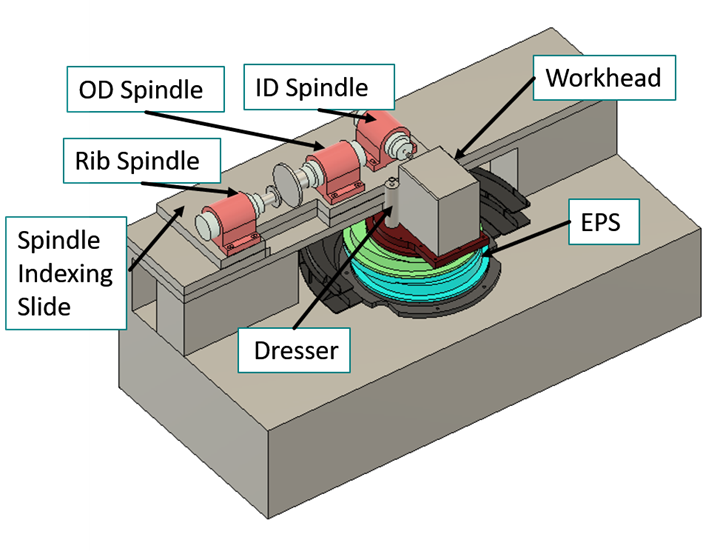
An example of the latter is the Eccentric Positioning System from Coventry Associates, an entirely novel grinding machine uses three circular rotary tables on top of each other rather than linear slide systems. These rotary tables have offset centers relative to one another, which enables them together to precisely guide both the linear and angular position of the grinding wheel for ID grinding applications, as shown in the video. This design is all electric, eliminating the need for hydraulics and the maintenance costs associated with them.
Using Circular Logic
By placing the grinding wheel on the rotary tables, Coventry enables the user to control its position in both the X and Z axes, as well as in a rotational axis. This high degree of control enables precise, complex passes, and the lack of hydraulic systems enabled the company to create this motion control with a footprint of 57×67 inches. “We actually took some old Heald size-1 grinding machine bases and built the EPS in those,” says Coventry Associates President Craig Gardner. “That base actually has more room than we need, so we can easily cut the footprint down 40% to meet customer needs.” Additionally, Gardner says that it is scalable to larger sizes.
“With a work envelope that is roughly twice that of a Heald 2CF machine, this machine was designed to grind bearings up to 24 inches in diameter,” says Gardner. The EPS positions within an 8.5-inch diameter circle, allowing the machine motion to inscribe a rectangle with 3 inches of X travel and 8 inches of Z travel. The remaining positioning area can be used for forming complex shapes in grinding wheels with the diamond dresser. However, Gardner anticipates that the company will be able to provide more solutions with the EPS design in the future.
“We are only just tapping into the array of solutions this shift in approach will bring.”
Despite its small size, the machine is comparatively rigid, according to the company. “The compact size of the EPS means that we have a very tight load path,” says Gardner. “The tight load path gives us a system with very high stiffness.”
One unique feature of the EPS is its ability to shape the grinding wheel without special tooling or formed diamond rolls. Because the machine maintains such a high degree of control over the wheel’s X, Z and angular position, it can shape the wheel with a standard single-point or rotary diamond-disc dresser, moving the wheel along the dresser to give it the desired shape. By eliminating the need for roll-form dressing, the system not only eliminates a cost associated with grinding, but makes the shop using it more adaptive, as there is no need to wait for formed diamond rolls to be made before starting on a customer’s part.
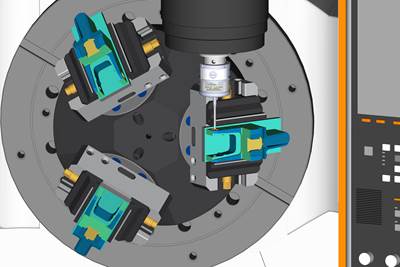
The multitool setup enables the user to perform multiple operations in a single setup with no tool changes or additional automation. All three grinding wheels in this example remain stationary as the EPS moves the workhead to grind the workpiece into shape. The workhead also holds the dresser, which can dress each wheel to whatever shape is required. Photo Credit: Coventry Associates
Additionally, the EPS does not necessarily need to attach the wheel to the rotary tables. Coventry has also developed a MultiTool version that places the part on the rotary tables and has three or more stationary grinding spindles around it. The EPS system feeds the workpiece into the stationary grinding spindles. “This approach enables the user to perform multiple operations with a single setup,” Gardner says. “You can, for example, grind the bore, race and rib of a tapered roller bearing cone in one setup.” This approach frees machine operators with comparatively little ancillary automation.
This cutaway of the EPS multitool shows how the rotary tables can position the workpiece with a high degree of accuracy. Photo Credit: Coventry Associates
Gardner recommends the SingleTool EPS with a single grinding wheel for high-production, low-volume work, while he prefers the MultiTool setup for high-mix, low-volume work.
Adaptable Controls for Precision Grinding
The Sinumerik 840D CNC from Siemens provides motion control. Gardner says adaptability figured into this choice. “For a system as novel as this, we needed a control that offers a great degree of customization,” he says. “The 840D provided us with the tools we needed to develop software for our unique kinematics.”

According to Coventry President Craig Gardner, the adaptability and customizability of the Siemens Sinumerik 840D enabled the company to control the unique kinematics of the EPS. Photo Credit: Siemens
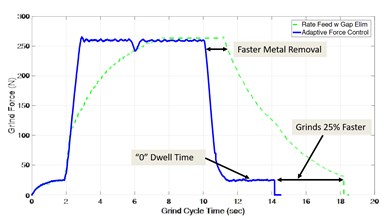
The software the company developed was the Maximizer Grinding Process, which includes features like the Adaptive Force Control (AFC), which maintains constant normal force during grinding. According to the company, constant normal force grinding increases the metal removal rate and reduces grind cycle time by up to 30%. “Studies have shown that the metal-removal rate is directly proportional to the normal grinding force,” says Gardner. “You want to grind at the highest normal grinding force the spindle power allows, provided you’re not burning the part.”
This figure shows a comparison between a grinding operation performed with Adaptive Force Control (blue line) and one performed with a rate-feed grind with a gap eliminator function (dashed green line). The AFC cycle time was 25% faster, thanks to its ability to quickly reach and maintain the optimal normal grinding force. Photo Credit: Coventry Associates
Another major feature of Coventry’s Maximizer software is its Real-Time Deflection Compensation. This feature compensates for the spindle and machine deflections that result in taper and part-to-part size variation. “Our real-time deflection compensation enables our system to hold in-process gage tolerances without an in-process gage.” says Gardner.
Part of the excitement many in Coventry feel is that they are only just tapping into the range of possibilities made available by the EPS. “What we have here is an entirely new solution to something as basic as how you position the tool (in case of the SingleTool) or the workpiece (for MultiTool),” Gardner says. “That is a fundamental change, which means that we are only just tapping into the array of solutions this shift in approach will bring.”
Related Content
SolidCAM iMachining and Technology Wizard: Faster Machining and Longer Tool Life
Smarter toolpaths to tackle modern machining challenges.
Read MoreSetting Up the Building Blocks for a Digital Factory
Woodward Inc. spent over a year developing an API to connect machines to its digital factory. Caron Engineering’s MiConnect has cut most of this process while also granting the shop greater access to machine information.
Read MoreThe Smarter Way to Take Full Control of Your CNC Machine Shop
Designed to bridge the gap between CAM programmers and shop floor operators, SolidShop provides a seamless, real-time solution for managing G-code, tracking production and eliminating costly mistakes.
Read More2 Secondary Coordinate Systems You Should Know
Coordinate systems tell a CNC machine where to position the cutting tool during the program’s execution for any purpose that requires the cutting tool to move.
Read MoreRead Next
New Applications for Electrochemical Grinding
With advances in control, sensor and automation technology, electrochemical grinding is more accurate and productive than ever, opening up new applications for the traditionally niche process.
Read MoreAn Introduction to Superfinishing
Learn what superfinishing is, what applications it should be used for and why you should take care when specifying surface finish parameters.
Read MoreSimulation Gets Real
Capability to generate something close to a true digital twin can significantly improve confidence in CAM program prove-outs.
Read More