Additive manufacturing is still a young development, and the different 3D printing processes it describes will continue to mature and advance alongside other significant manufacturing trends. AM is particularly well-suited to helping companies adopt more digital and flexible production, as well as more sustainable manufacturing operations. By utilizing only the material necessary, supporting the creation of lightweight and efficient parts, and enabling new end-of-life opportunities for used products, additive manufacturing can support efforts toward sustainability and the circular economy.
The digital nature of the process and its lack of tooling also makes it particularly well-suited for distributed or decentralized manufacturing, in which production is spread throughout many facilities rather than centralized in one location. This model supports localized production near where customers are, reducing shipping and establishing shorter, more secure supply chains. The concept is still new, but was seen in practice in the early part of 2020 when a consortium of U.S. 3D printing companies was formed to develop and manufacture nasopharyngeal swabs needed for COVID-19 testing, as detailed in the below video (a special episode of The Cool Parts Show).
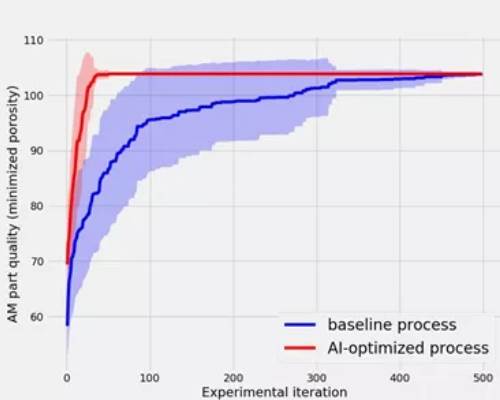
In addition to supporting larger trends in manufacturing, AM also stands to benefit from technological advances. As a digital manufacturing method, 3D printing can become more predictable and accurate in combination with improved simulation tools and control software. Machine learning, in particular, is a natural complement to industrial 3D printing.