The Value of Design for Additive Manufacturing (DFAM)
Design is the “value multiplier” when it comes to additive manufacturing.
Share


It can be hard to put a value on something, particularly the products a company makes or the parts someone designs. Cost, on the other hand, is easy. We know exactly how much a machine or material costs because we have to pay for it when we buy it. We can even get a reasonably good estimate for the cost to develop a product because we can count how many hours it took to engineer it, the cost to make prototypes, the cost to test each prototype, etc.
While these efforts add value to the product as it is being developed, quantifying that value is challenging. If the product does well in the marketplace, then we know that those efforts added value, but how much value was added at each stage of development remains open to interpretation.
If you read my column last month, I proposed a simple cost equation for additive manufacturing (AM) using laser powder-bed fusion (PBF), one of the more popular AM processes right now for fabricating metal parts layer by layer. While reading about an equation may not excite you, that equation helps us unlock the value of design for AM, or DFAM as it is called in the industry.
What do I mean? The four main components of my AM cost equation are material, build time, machine cost and pre/postprocessing costs. The more material needed, the more the part will cost; that one is easy. Build time and machine cost are a bit more coupled. Longer build time equates to higher cost, but a more expensive machine (e.g., a laser PBF system with multiple lasers) costs more to operate and offers a faster build rate. Of course, the maximum height of the part being built also adds build time and subsequent machine cost since the recoater takes about 10 seconds to spread a new layer of powder. This “dead time” and associated cost may seem trivial, but when you are spreading thousands of layers, it can become significant. Finally, pre- and postprocessing costs were estimated at roughly 40% of the overall cost for an AM part based on recent industry averages.
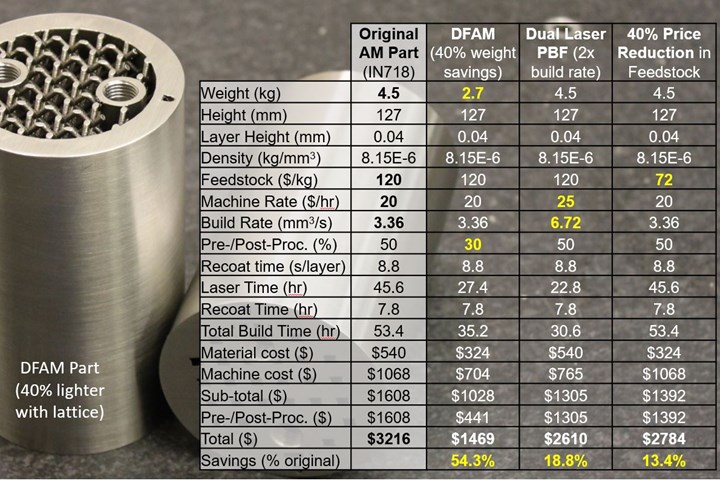
While lower powder prices and faster build speeds are great, it is easy to see why DFAM is the best value multiplier when it comes to AM.
With this model, the total cost of a metal AM part made using laser PBF can be estimated as the sum of material and machine costs, the latter of which is a direct function of the build time and layer recoating time, all divided by one minus the percentage of cost attributed to pre/postprocessing. To make the math easy for now, let us assume that pre/postprocessing cost is 50% so that we simply double the sum of material and machine cost to estimate the total cost of a metal AM part.
With this simple equation in mind, it becomes easy to quantify the value of DFAM in terms of the savings it imparts on the cost of a metal AM part. We can also compare that savings to the savings from other factors, such as reductions in the cost of powder feedstock or the productivity gains from having more lasers or other improvements that increase build speed.
Let’s start with the latter two. If the cost of powder feedstock is reduced by 10-20%, then the material cost is also reduced by 10-20%. These savings translate directly to the total cost when we apply our pre/postprocessing multiplier, but only in proportion to the ratio of material cost to machine cost. For example, if material cost and machine cost contribute equally to the part cost, which may be the case for an expensive material like titanium, then the total cost is reduced by 5-10% after applying our pre/postprocessing assumption since only half of the costs are attributed to the material.
The same logic applies to build speed. If the build speed doubles, then the build time (i.e., the laser exposure time) is reduced, but not by 50% since we still have the recoating time. A short part (low z height) may see a 45% reduction in build time while a tall part (high z height) may only see a 30% reduction instead of the 50% or 75% savings you might expect. Unfortunately, the hourly cost of a multi-laser PBF system may be 50-100% more than a single-laser system, and the cost savings from reduced build time are not as high as you would expect. For the sake of argument, let us say doubling the build rate leads to 30% savings in machine cost for a metal AM part. As with material, this savings translates to the final cost in proportion to the ratio of material cost and machine cost after applying our pre/postprocessing multiplier. Assuming a 50/50 split, the final cost would be reduced by 15% in this scenario.
Now, how does DFAM compare? Well, if we use DFAM to lightweight a structure as is often done, then we save weight, which reduces material cost. It also means less volume to build, which reduces laser exposure and build time, lowering machine cost without increasing the hourly machine rate. DFAM also reduces the amount of support material needed, which further reduces material cost, build time and machine costs. Assuming preprocessing cost lies in build setup and prep, not the non-recurring engineering (i.e., design, optimization, analysis), then less support material means less build prep. More importantly, fewer supports means less postprocessing costs because you do not waste as much time removing them after the build. As such, DFAM also reduces pre/postprocessing costs, decreasing the cost multiplier, saving more cost and increasing the value of DFAM even more. The example in the figure shows how a 40% weight savings from using a lattice structure offers 3 to 4 times the value compared to doubling the build speed or a 40% reduction in the cost of powder feedstock.
While lower powder prices and faster build speeds are great, it is easy to see why DFAM is the best value multiplier when it comes to AM. DFAM simultaneously reduces the cost of materials, the build time, the machine cost, and percentage of pre/postprocessing costs, compounding the savings many times over. More importantly, DFAM is something that you can control — you are not at the mercy of a powder supplier or a machine manufacturer to lower the price for you. In other words, if you are investing in AM, make sure to invest in DFAM (e.g., software, tools, training) as it will multiply the value of AM many times over.
Related Content
The Downloadable Metal 3D Printer
Copenhagen researchers introduce a fully open-source laser powder bed fusion system, now available on GitHub. This release follows their development of an open-source vat polymerization machine. Here is the purpose and promise of this philanthropically funded effort to advance additive manufacturing application and adoption.
Read MoreAdditive/Subtractive Hybrid CNC Machine Tools Continue to Make Gains (Includes Video)
The hybrid machine tool is an idea that continues to advance. Two important developments of recent years expand the possibilities for this platform.
Read MoreMachine Tool Drawbar Made With Additive Manufacturing Saves DMG MORI 90% Lead Time and 67% CO2 Emission
A new production process for the multimetal drawbar replaces an outsourced plating step with directed energy deposition, performing this DED along with roughing, finishing and grinding on a single machine.
Read MoreHow to Meet Aerospace’s Material Challenges and More at IMTS
Succeeding in aerospace manufacturing requires high-performing processes paired with high-performance machine tools. IMTS can help you find both.
Read MoreRead Next
How 3D Printing Enables More Sustainable Designs (Video #2)
The circular economy needs the lightweight, optimized and efficient designs that only 3D printing can provide. More in this video, part of our series on 3D Printing and the Circular Economy.
Read More3D Printed Ceramics Serve As Both Bone Graft and Support
Bioceramics including tricalcium phosphate and zirconia have been used to replace and stabilize human bone in reconstructive surgeries. Now, 3D printing brings customization and new design opportunities to these medical devices.
Read MoreWhat Do These Flip Flops Say About Manufacturing's Future?: The Cool Parts Show #21
These 3D printed flip-flops are an example of mass customization, but they also hint at manufacturing's more sustainable, circular future. Find out why in this episode of The Cool Parts Show.
Read More