Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
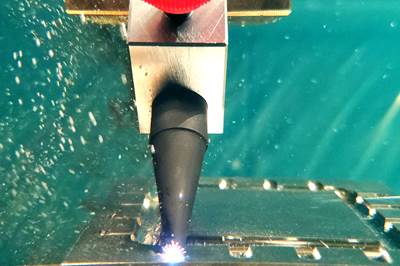
EDM, or electrical discharge machining, is capable of machining complex shapes in hard materials. The process includes an electrode and a workpiece, both submerged in dielectric fluid. Electrical current flows between the workpiece and electrode, repeatedly creating tiny plasma zones that instantaneously melt and remove the material. The electrode in EDM takes different forms. Wire EDM machines use a thin wire to cut. Ram EDM machines, or “die sinkers,” use electrodes that are custom machined into 3D shapes. The EDM process produces a cavity in the part that is the opposite or female version of the “male” electrode form. Similar to the ram EDM machine is the small-hole EDM machine, or “hole popper.” On this machine, the electrode is a cylinder used to machine a hole.



ESSENTIAL READING
VIEW ALLWhen Organic Growth in Your Machine Shop Isn’t Enough
Princeton Tool wanted to expand its portfolio, increase its West Coast presence, and become a stronger overall supplier. To accomplish all three goals at once, acquiring another machine shop became its best option.
Read MoreMachining 101: What is Electrical Discharge Machining?
Electrical discharge machining, or EDM, is a non-contact form of machining that projects sparks from an electrode or wire to vaporize material of any hardness.
Read MoreCool Tricks: How to Photograph Sinker EDM
Sometimes it takes a little extra effort and ingenuity to solve a problem. In the case of the February 2020 cover of Modern Machine Shop, it took a lot of each — and a cheap plastic spaghetti container.
Read MoreInside the Sinker EDM Process, One Spark at a Time
Successful sinker EDM operations rely on understanding the relationship between each individual spark, the electrode and the workpiece.
Read MoreCAM Simulation Gets Toolmaker up to Speed with B-Axis EDM
Software simulation helped this machine shop learn how to program its new advanced, high-tolerance wire EDM. The software also helped the shop turn job quotes around quickly.
Read MoreBuying a Wire EDM, Part 4: Dielectric Fluid & Maintenance
Removing the microscopic particles made during the wire EDM cutting process becomes a key factor in maximizing cutting speed as well as attaining part accuracy and surface finish. Dielectric fluid is the mechanism for flushing these “chips” away.
Read MoreLatest EDM News And Updates
MC Machinery Displays EDM, Precision Milling, 3D Printing
IMTS 2024: MC Machinery Systems showcases an array of EDM and precision milling tools, as well as a wire laser metal 3D printer.
Read MoreBelmont Small-Hole EDM Features Multitasking Capabilities
The SY-4060 provides automatic depth control, three-step control of EDM parameters and conversational G- and M-code programming.
Read MoreGF Machining Solutions Celebrates 70 Years of EDM Technology
GF Machining Solutions is celebrating the 70th anniversary of its discovery of EDM Technology.
Read MoreElectrical Discharge Machining in Ten Articles
This roundup of the top ten Electrical Discharge Machining articles on Modern Machine Shop covers the wide range of EDM topics.
Read MoreHybrid Control Makes Lights-Out EDM More Accessible
This CNC enables EDMs to switch between G-code and an integrated CAM system to adapt to changing conditions and make lights-out manufacturing more attainable.
Read MoreEDM Network Wire EDM Features Four-Axis Cutting
The EDMMax 434W fast-wire EDM includes four-axis cutting capability that enables it to cut 3D support structures or other shop-related parts.
Read MoreFeatured Posts
EDM, Laser Micromachining and More at GF Medical Demo Center
At GF’s Medical Center of Competence, the company shows off EDM and laser features that could make a large impact on medical manufacturing — and elsewhere.
Read MoreDielectric Oil Dramatically Reduces EDM Maintenance
Plagued by repeated small fires that interrupted its wire EDM throughput, this cutting tool manufacturer changed its dielectric oil and both eliminated fires and reduced its oil consumption.
Read MoreWhen Organic Growth in Your Machine Shop Isn’t Enough
Princeton Tool wanted to expand its portfolio, increase its West Coast presence, and become a stronger overall supplier. To accomplish all three goals at once, acquiring another machine shop became its best option.
Read MoreRobot Frees EDM Drill From Machine Enclosure
CNC integration with a six-axis arm provides precise enough positioning to shape air- and gas-flow holes in aerospace and power generation parts.
Read MoreAutomation Adds Capacity to Capability for Low-Volume Work
Investment in machining technology has facilitated growth and diversification at Reich Tool & Design. Now, flexible automation allows the shop to get more out of its machines despite a shortage of skilled workers.
Read MoreFive Reminders For Machining Graphite
Graphite machining can be a tricky business, so keeping certain issues top of mind is vital to productivity and profitability.
Read MoreFAQ: EDM
What is EDM?
Electrical discharge machining, or EDM, is a non-contact process that can machine parts regardless of their hardness. It involves placing an electrode or wire and an electrically conductive workpiece into a circulating dielectric fluid. The fluid acts as an insulator until a specific spark gap and voltage ionizes it and enables a spark to travel to the workpiece.
Using a CNC, the operator moves the electrode or wire as needed and rapidly turns the current on and off. This accommodates the flushing of molten material (often called “swarf”) from the workpiece.
Source: Machining 101: What is Electrical Discharge Machining?
What are the two types of EDM machines?
The two main types of EDM machines are sinker EDM machines and wire EDM machines.
Source: Machining 101: What is Electrical Discharge Machining?
What is sinker EDM?
Sinker EDM uses an electrode as its “cutting” tool, with the shape of the electrode serving as a mirrored, slightly smaller image of the finished form it will produce in the workpiece. The electrode makes one spark at a time — but the frequency of the current means the tool could produce anywhere between 500 and 30,000 sparks per second.
Electrodes for sinker EDM are typically either copper or graphite.
Source: Machining 101: What is Electrical Discharge Machining?
What is wire EDM?
Wire EDM feeds a strand of wire from a supply spool to the workpiece via a wire drive system. The wire is energized by electrical contacts and passes through the workpiece at a specific velocity determined by the operation at hand. A stream or bath of deionized water surrounds the wire, and sparks are continuously emitted along the length of the wire. Rollers pinch the wire and provide tension, while guides above and below the workpiece position the wire on its path — helping it to achieve complex shapes on the workpiece.
The wires used in this process commonly have diameters of 0.010 to 0.012 inch, with finer wires at 0.001 to 0.004 inch. The material of the wires also holds great influence over the operation’s success, as hard wires that have insufficient tensile strength for an operation are liable to break under sudden shock. Softer wires prove more desirable for high-taper cutting operations.
Source: Machining 101: What is Electrical Discharge Machining?
What is swarf?
During the EDM process, the operator moves the electrode or wire as needed and rapidly turns the current on and off. This accommodates the flushing of molten material (often called “swarf” or “chips”) that is removed from the workpiece.
Source: Machining 101: What is Electrical Discharge Machining?