The Case For Integrated Control Of Machining Operations
An integrated software system automates a decision-making process that helps a machinist inspect parts on a timely basis, offset or change tools and appeal to engineers for improvement of process design.
Share



Many shops have implemented computerized systems to gather data for production reporting, quality control, SPC and tool management. Dr. Stephen Birman, president of High Tech Research, Inc. (Deerfield, Illinois) believes one knowledge-based system that integrates all of these functions can create a level of operational control that delivers otherwise unattainable benefits. Not surprisingly, this holistic concept is behind the Micronite software that his company offers.
His definition of integration goes beyond simply getting separate shop control, inspection and tool control systems to share data to help managers make better decisions and streamline operations. He contends that a complete "production loop" should intertwine automated downtime monitoring, shopfloor-based process control, error-proof quality assurance and proactive operations management. This intelligent loop enables machinists to control machining output efficiently and effectively. Result-oriented interactive control, he says, prevents not only the production of out-of-tolerance parts, but also wasted tool life and unnecessary production stoppages. The net result is at least a 10-percent reduction in production costs, elimination of human errors and increased throughput.
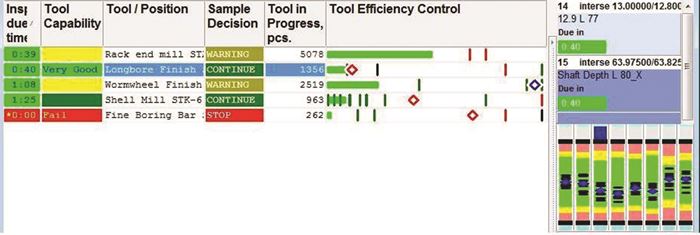
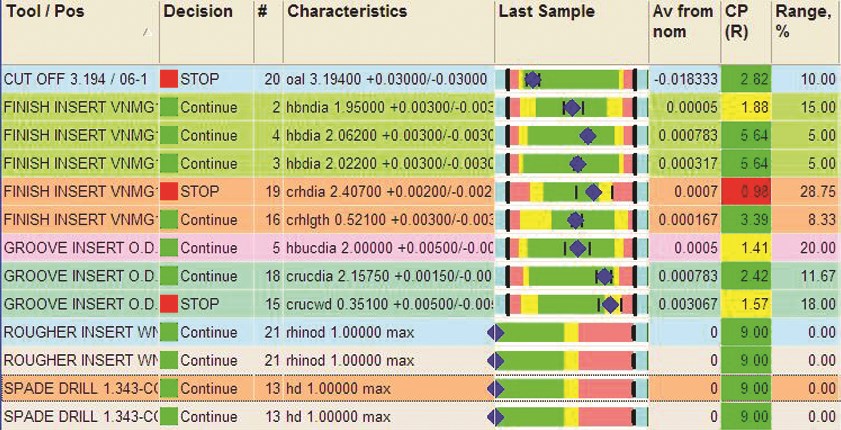
According to Dr. Birman, the key is using system-supervised data capture to determine the process profile for modeling tool wear and variation patterns and then dynamically adjusting the frequency of part sampling. The Micronite system automates a decision-making process that helps a machinist inspect parts on a timely basis, offset or change tools and appeal to engineers for improvement of process design. In essence, the software uses the data to create a knowledge base about each monitored operation and the performance of the related cutting tool. "The system turns the shop floor into a machining lab from which data can be analyzed and used as the ‘science’ behind decision making," Dr. Birman says. Accuracy of process decisions and the appropriateness of corrective actions are further reinforced by using sampling results and the growing body of tooling information in the database. He calls this approach "adaptive tool life expectancy."
In the Micronite system, different predictive models are applied to specific machining processes, equipment, materials, lot sizes and so on. There are special models for small-batch production, super-precision components, hard-to-machine materials and multi-functional tools. For example, operations in which one cutting tool is associated with one workpiece dimension require a different control strategy than operations involving a cutting tool that creates multiple dimensions. These strategies are tailored for each situation so that data can be analyzed appropriately and behavior predicted accurately. As artificial intelligence in the software determines the non-linear trends emerging in the data, it may change the frequency of part sampling. This allows the system to reliably detect when accelerated tool wear is beginning to occur. At this point, the system automatically tells the operator to stop the process. This happens before defective parts are made but not before the tool is truly approaching the end of its useful life.
Dr. Birman points out that an integrated operations control system belies some of the myths that plague other control philosophies. For example, many systems based on solely statistical process control (SPC) assume that any machining process can be run under a state of statistical control. Unfortunately, he says, this assumption is contrary to the dynamics of most machining operations, which are non-linear and non-repetitive in nature. This precludes use of SPC either for machining process control or for assurance of precise component quality.
Furthermore, SPC advises that monitoring efforts should concentrate on control of the tightest tolerances. If these tolerances can be held, it is assumed, wider tolerance bands will also be under control. The flaw in this approach, Dr. Birman says, is that a tighter tolerance created by a multi-functional tool may be more stable than ones involving looser tolerances. Thus, SPC techniques may not ensure that defective parts will not be produced. The data gathering and intelligent analysis techniques in the Micronite system, however, treat each machining and grinding operation according to its own distinctive
characteristics.
Related Content
Setting Up a Small Shop for Big Growth
Metal Trade Solutions is laying a foundation to grow by determining standard tools and workholding, and fully implementing technology.
Read MoreHow a Family-Owned Tooling Company Competes with Global Giants (Includes Video)
Not ready to go digital? Consider this: With Siemens NX ecosystem, precision shop D’Andrea cut its programming time by 50% and is able to compete globally—even against industry giants.
Read MoreBenefitting From an Accurate Data Ecosystem
Data is useless unless it’s true. After decades of false starts with incomplete, unstandardized data collection systems, Alexandria Industries put together a software ecosystem that delivers accurate data to managers, operators and ERP systems alike. In this article, discover its effect on the Alexandria shop floor.
Read MoreScaling Up Without Starting From Scratch
In its quest to become a single source for all its customers, sheet metal fabricator GTR Manufacturing long considered bringing machining in house, but a lack of space and expertise held it back – until it found the perfect solution.
Read More
















.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)








