-
-
SPONSORED
-
SPONSORED
-
Laser & Waterjet
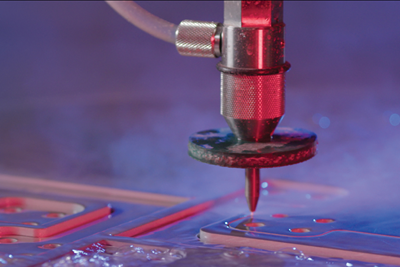
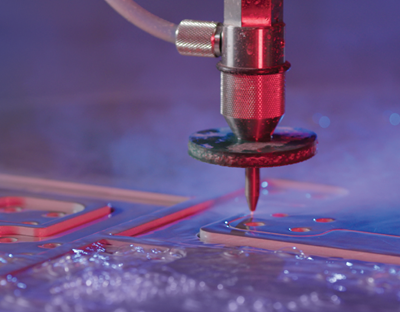
In waterjet cutting, the material removal operation can be described as a supersonic erosion process. It is not pressure but steam velocity that tears away microscopic pieces or grains of material. To achieve high-stream velocity, the pressurized water passes through a tiny hole in a jewel that is affixed to the end of the plumbing tubing. Lasers are systems for the generation and amplification of light, where “light” can refer to any electromagnetic wavelength. In its simplest form, a laser consists of a gain medium, a method of pumping the gain medium and an optical cavity.




ESSENTIAL READING
VIEW ALLWhen Laser Cutting Precision Begins with the Quote
A harmonious marriage of CNC machining and sheet-metal fabricating equipment depends on identifying the right process and the right price for every part.
Read MoreWhat is Laser Cleaning? How Does it Work? EMAG Experts Explain
Lasers provide the flexibility to clean some areas of a CNC-machined workpiece while leaving others untouched.
WatchMachining 101: What is Waterjet Cutting?
Waterjet cutting may be a simpler machining method, but it packs a powerful punch that requires operators to stay cognizant of multiple parts’ wear and accuracy.
Read MoreWeep Not, Waterjet Machine. Predictive Maintenance is Here.
The versatility of waterjet cutting is well known, but its reputation as a maintenance intensive technology holds it back. Predictive maintenance may change that.
Read MoreLaser Versus Waterjet for 2D Metalcutting
When should you choose laser cutting over waterjet, and vice versa? A metal fabricator offers some guidelines.
Read MoreWhy Not Start With Waterjet?
In titanium, significant savings and process efficiency can result from the simple fact that abrasive waterjet cutting leaves the remaining stock intact.
Read MoreLatest Laser & Waterjet News And Updates
Hypertherm Waterjet Technology Supports Smart Factory Implementation
Hypertherm Associates' Omax advanced abrasive waterjet systems provide versatile, easy-to-use solutions for manufacturers.
Read MoreUnited Grinding Laser Machine Enhances Precision Tool Processing
United Grinding North America Inc.’s Vision Laser offers advanced laser technology for brazed tools with high-quality requirements and versatile applications.
Read MoreHypertherm Doubles Warranty Length for Plasma Cutters
Powermax plasma cutters feature extensive manual and automated metalcutting and gouging capabilities.
Read MoreOmax Waterjet Machine Eliminates Need for Secondary Machining
Eastec 2025: The Maxiem 1530 JetMachining Center is designed to deliver versatile, easy to use machining from prototype development to full-scale production.
Read MoreFlow Waterjet Cutting System Provides Fast Overall Cut Time
IMTS 2024: Flow’s Mach 200c five-axis cutting system features high-speed motors and drives for rapid speed and acceleration and deceleration.
Read MoreHamar Laser Instruments Surface Plate Calibration System Increases Repeatability
IMTS 2024: Hamar Laser Instruments introduces the L-703SP surface plate calibration system, intended to reduce time for surface plate calibration by 30 to 60%.
Read MoreFeatured Posts
Robot-Ready Laser Marking Machines Hit the Show Floor
Laser Marking Technologies LLC (LMT) is highlighting its robot readiness not only in its booth but also in its customers’ booths and partners Universal Robots and FANUC booths.
Read MoreWhere Micro-Laser Machining Is the Focus
A company that was once a consulting firm has become a successful micro-laser machine shop producing complex parts and features that most traditional CNC shops cannot machine.
Watch3 Lessons Job Shops Can Learn From Laser Cutters
This laser-cutting “job shop” designs its processes to make high-mix, low volume work profitable.
Read MoreEDM, Laser Micromachining and More at GF Medical Demo Center
At GF’s Medical Center of Competence, the company shows off EDM and laser features that could make a large impact on medical manufacturing — and elsewhere.
Read MoreNo Longer a Last Resort: Conference Focuses in on Laser Applications
Wednesday’s Industrial Laser Conference is all about lasers, their benefits and applications. Sessions start at 9:30 a.m. in the West Building – so you still have time to register!
Read MoreIndustrial Fiber Laser Solutions for Marking and Traceability
IMTS22: Dapra’s latest industrial-grade fiber laser marking and engraving technology provides reliable performance, fast cycle times and outstanding flexibility to fit any manufacturing environment.
Read MoreFAQ: Laser & Waterjet
What is laser cutting?
Laser micromachining includes processes like laser ablation, where the laser energy penetrates the material and leads to some transformation. Laser ablation is the direct removal of material resulting from the interaction of the laser light with the sample. Most commonly, ablation relies on the laser light being absorbed in the material, leading to material interaction.
Source: Modern Machine Shop’s Handbook for the Metalworking Industries
What is waterjet cutting?
Waterjet cutting, at its simplest, is the process of a high-pressure jet of water cutting into a material. The technology often compliments other machining techniques such as milling, laser, EDM and plasma. No hazardous material or vapors form during the waterjet process, and neither do heat-affected zones or mechanical stresses. Waterjet can cut whisper-thin details in stone, glass and metals; quickly drill holes in titanium; cut food; and even kill pathogens in beverages and dips.
What are potential errors to watch for with waterjet cutting?
Potential errors affecting accuracy include cutter compensation error, programming error and machine motion.
Cutter compensation is the value entered into the control system to take into account the width of cut from the jet — that is, the amount by which the cut path must be enlarged so the final part comes out the proper size. To avoid potential errors in high-precision work, the operator should conduct test cuts and know the frequency at which cutter compensation must be adjusted to match mixing tube wear.
Programming errors arise most often because some XY controls do not show dimensions on part programs, making lack of dimensional matching between the part program and the CAD drawing difficult to detect. Important aspects of machine motion that can introduce errors are backlash in the mechanical unit and repeatability.









































.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)


